It may be easy, even comforting, to imagine that using AI tools involves interacting with a purely objective, stoic, independent machine that knows nothing about you. But between cookies, device identifiers, login and account requirements, and even the occasional human reviewer, the voracious appetite online services have for your data seems insatiable.
Privacy is a major concern that both consumers and governments have about the pervasive spread of AI. Across the board, platforms highlight their privacy features—even if they’re hard to find. (Paid and business plans often exclude training on submitted data entirely.) But any time a chatbot “remembers” something can still feel intrusive.
In this article, we will explain how to tighten your AI privacy settings by deleting your previous chats and conversations and by turning off settings in ChatGPT, Gemini (formerly Bard), Claude, Copilot, and Meta AI that allow developers to train their systems on your data. These instructions are for the desktop, browser-based interface for each.


ChatGPT
Still the flagship of the generative AI movement, OpenAI’s ChatGPT has several features to improve privacy and alleviate concerns about user prompts being used to train the chatbot.
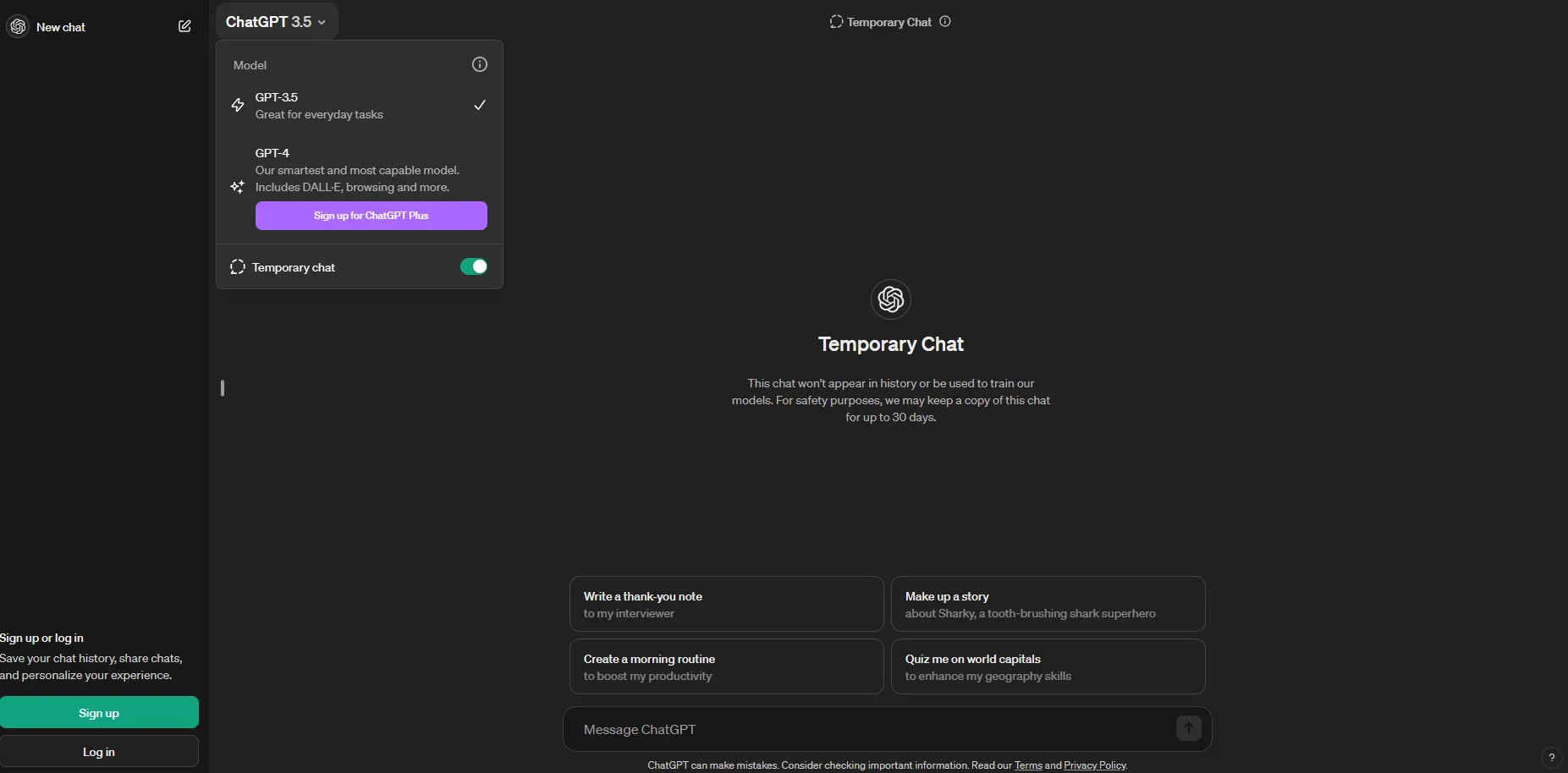
In April, OpenAI announced that ChatGPT could be used without an account. By default, prompts shared through the free, account-less version are not saved. But, if a user does not want their chats used to train ChatGPT, they still need to toggle the “Temporary chat” settings in the ChatGPT dropdown menu at the top left of the screen.
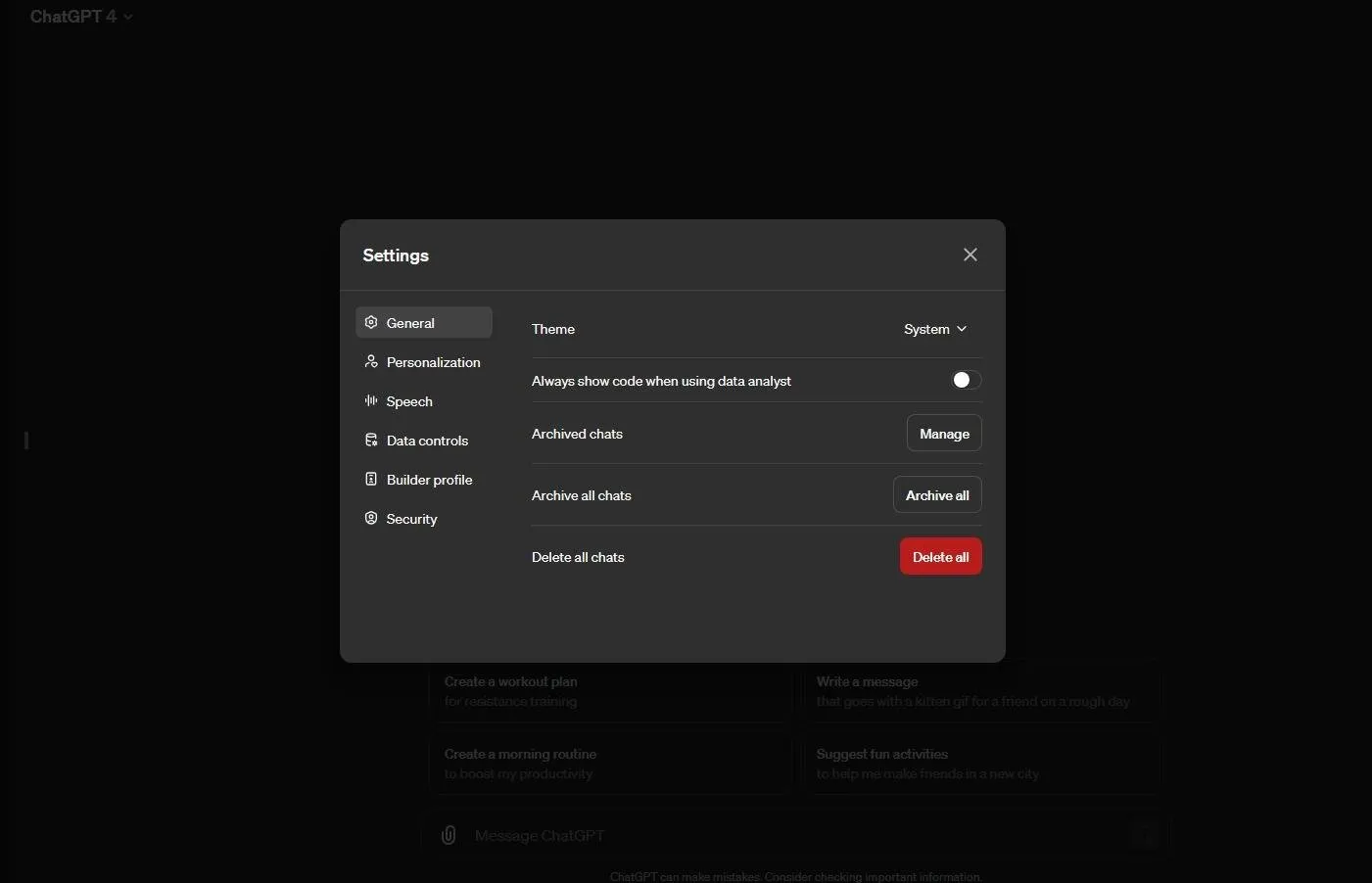
If you have an account and subscription to ChatGPT Plus, however, how do you keep your prompts from being used? GPT-4 gives users the ability to delete all chats under its general settings. Again, to make sure chats are also not used to train the AI model, look lower to “Data controls” and click the arrow to the right of “Improve the model for everyone.”
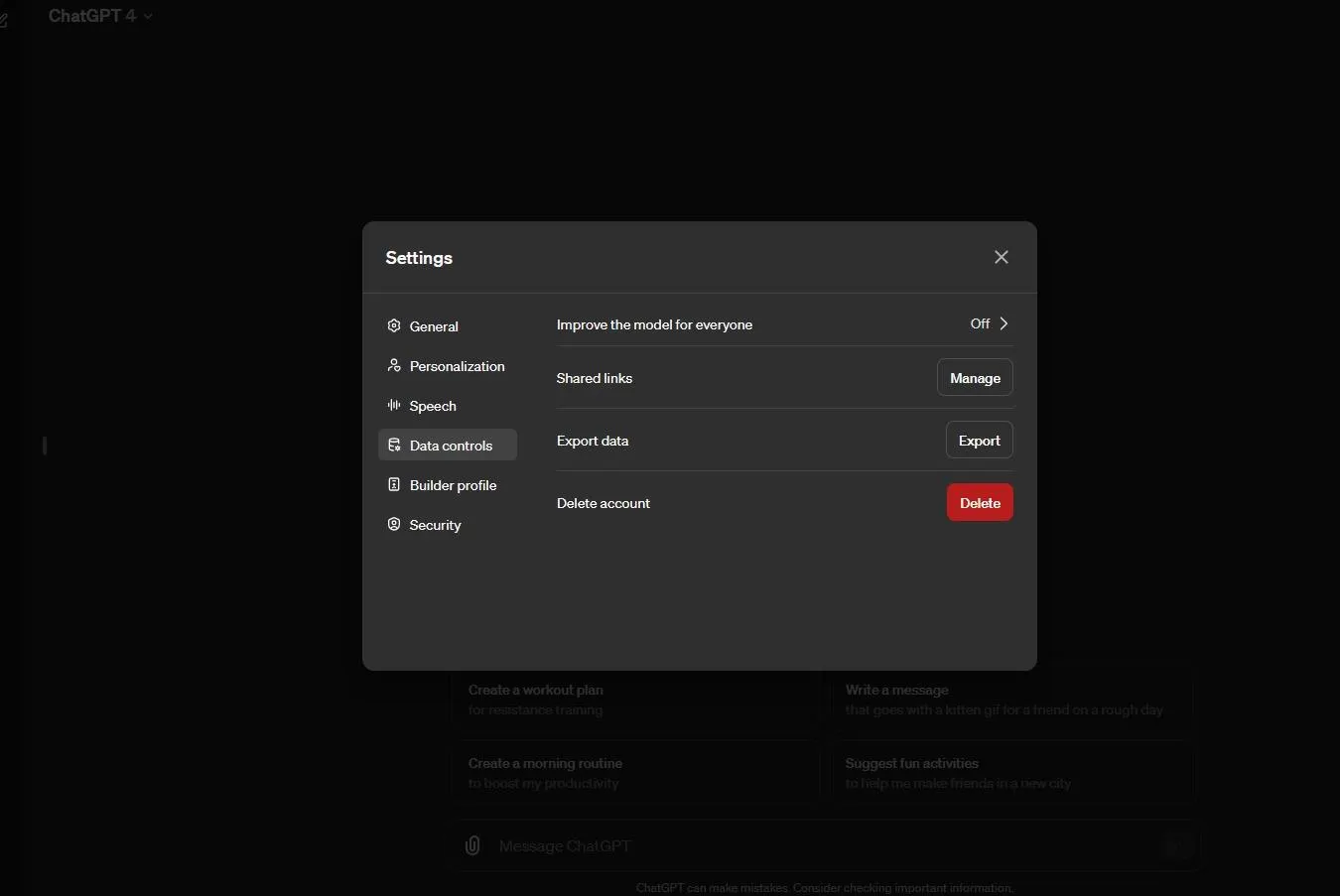
A separate “Model improvement” section will appear, allowing you to toggle it off and select “Done.” This will remove the ability of OpenAI to use your chats to train ChatGPT.
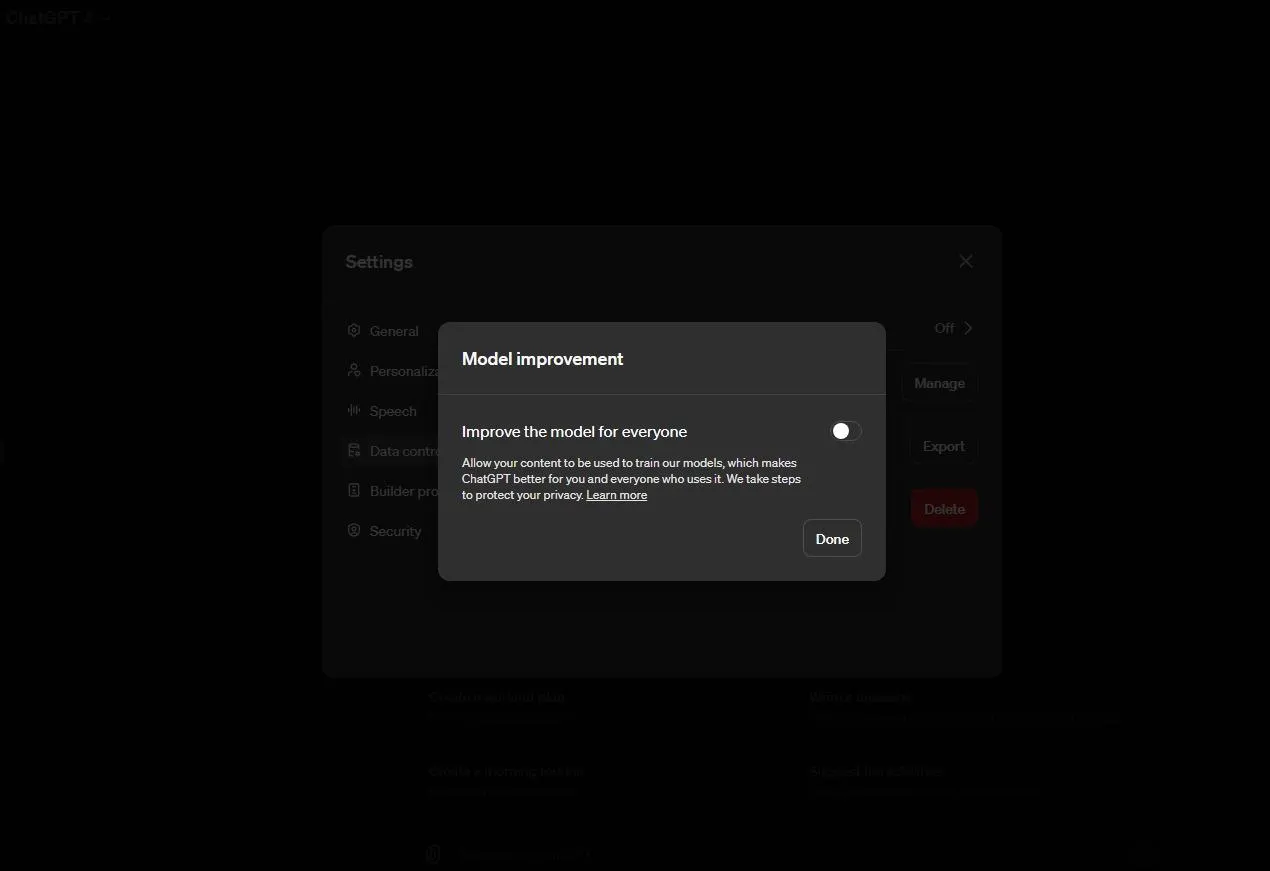
There are still caveats, however.
“While history is disabled, new conversations won’t be used to train and improve our models, and won’t appear in the history sidebar,” an OpenAI spokesperson told Decrypt. “To monitor for abuse—and reviewed only when we need to—we will retain all conversations for 30 days before permanently deleting.”
Claude
“We do not train our models on user-submitted data by default,” an Anthropic spokesperson told Decrypt. “Thus far, we have not used any customer or user-submitted data to train our generative models, and we’ve expressly stated so in the model card for our Claude 3 model family,”
“We may use user prompts and outputs to train Claude where the user gives us express permission to do so, such as clicking a thumbs up or down signal, on a specific Claude output to provide us feedback,” the company added, noting that it helps the AI model “learn the patterns and connections between words.”
Deleting archived chats in Claude will also keep them out of reach. “I do not retain or have access to any previously deleted chats or conversations,” the Claude AI agent helpfully answers in the first person. ”My responses are generated based on the current conversation only.”
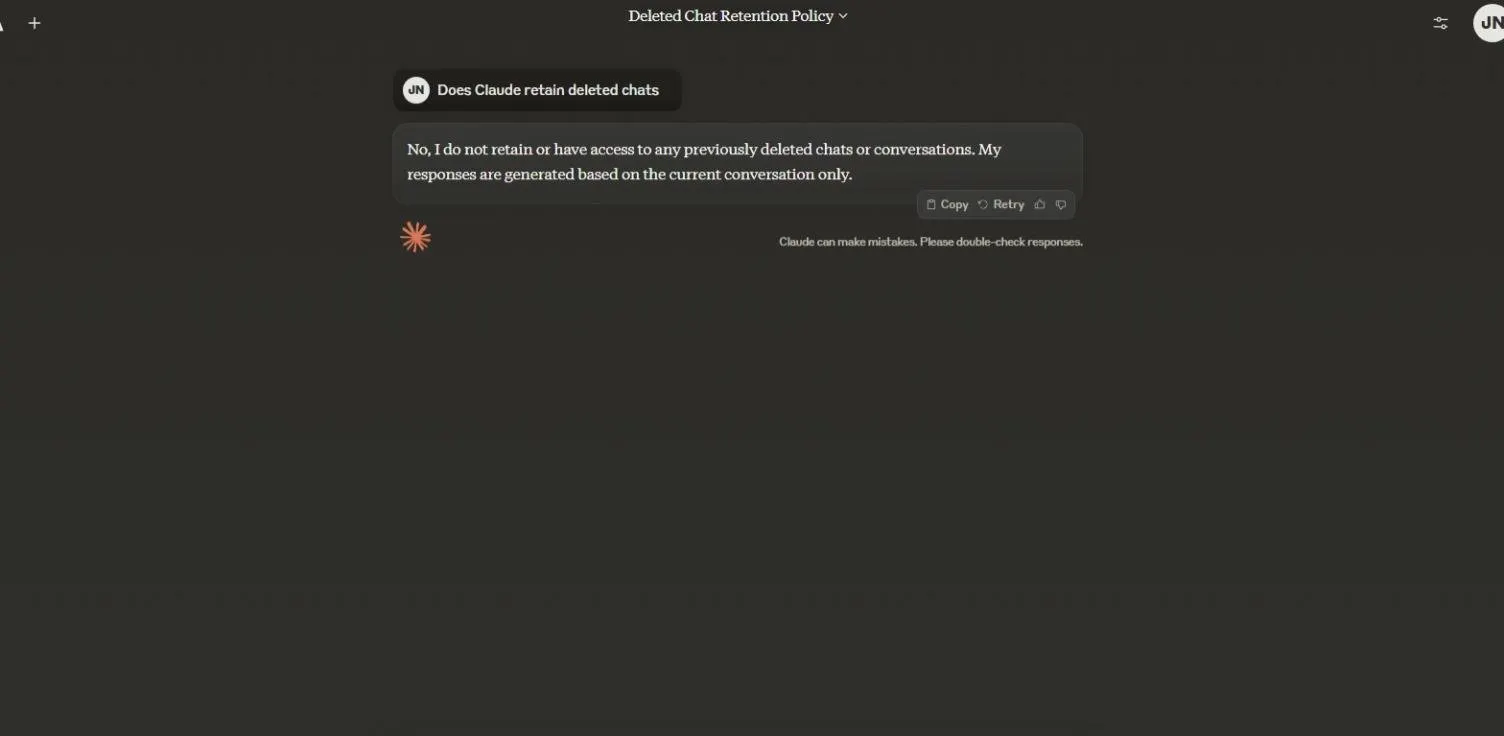
Like ChatGPT, Claude does hold on to some information as required by law.
“We also retain data in our backend systems for the amount of time specified in our Privacy Policy unless required to enforce our Acceptable Use Policy, address Terms of Service or policy violations, or as required by law,” Anthropic explains.
As for Claude’s collection of information across the web, an Anthropic spokesperson told Decrypt that the AI developer’s web crawler respects industry-standard technical signals like robots.txt that site owners can use to opt-out of data collection, and that Anthropic does not access password-protected pages or bypass CAPTCHA controls.
Gemini
By default, Google tells Gemini users that “your conversations are processed by human reviewers to improve the technologies powering Gemini Apps. Don’t enter anything that you wouldn’t want to be reviewed or used.”
But Gemini AI users can delete their chatbot history and opt out of having their data used to train its model going forward.
To accomplish both, navigate to the bottom left of the Gemini homepage and locate “Activity.”
Once on the activity screen, users can then turn off “Gemini Apps Activity.”
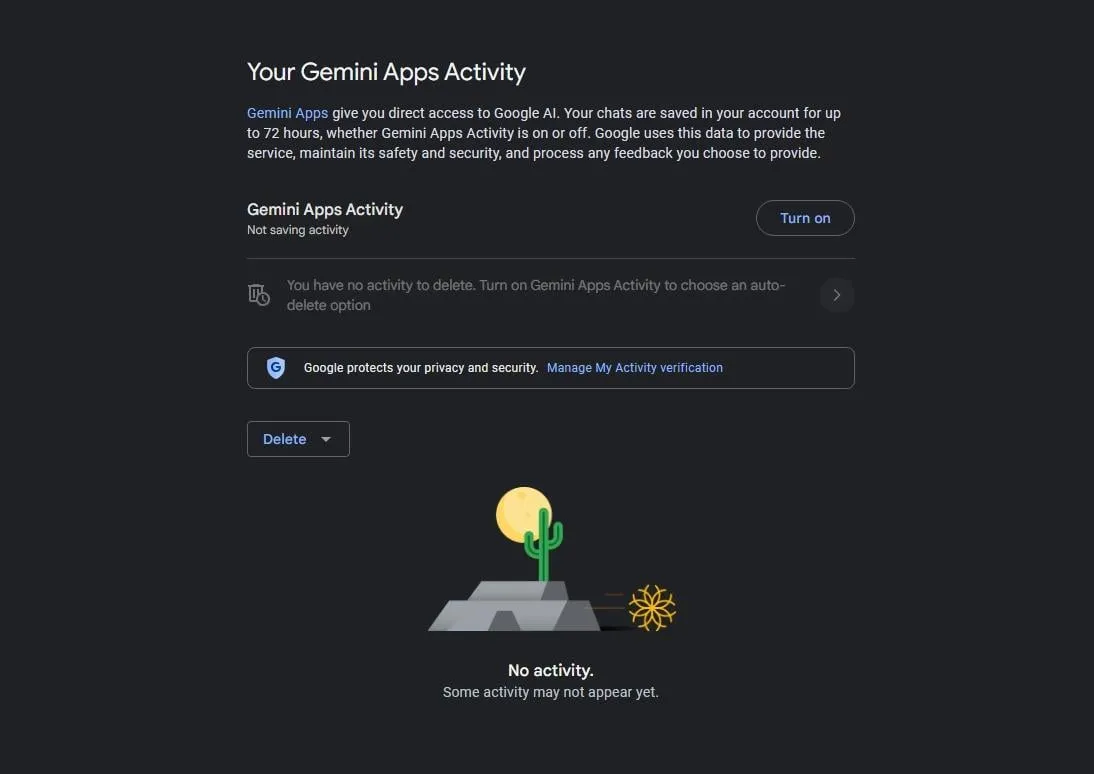
A Google representative explained to Decrypt what the “Gemini Apps Activity” setting does.
“If you turn it off, your future conversations won’t be used to improve our generative machine-learning models by default,” the company representative said. “In this instance, your conversations will be saved for up to 72 hours to allow us to provide the service and process any feedback you may choose to provide. In those 72 hours, unless a user chooses to give feedback in Gemini Apps, it won’t be used to improve Google’s products, including our machine learning technology.”
There is also a separate setting to clear out your Google-connected YouTube history.
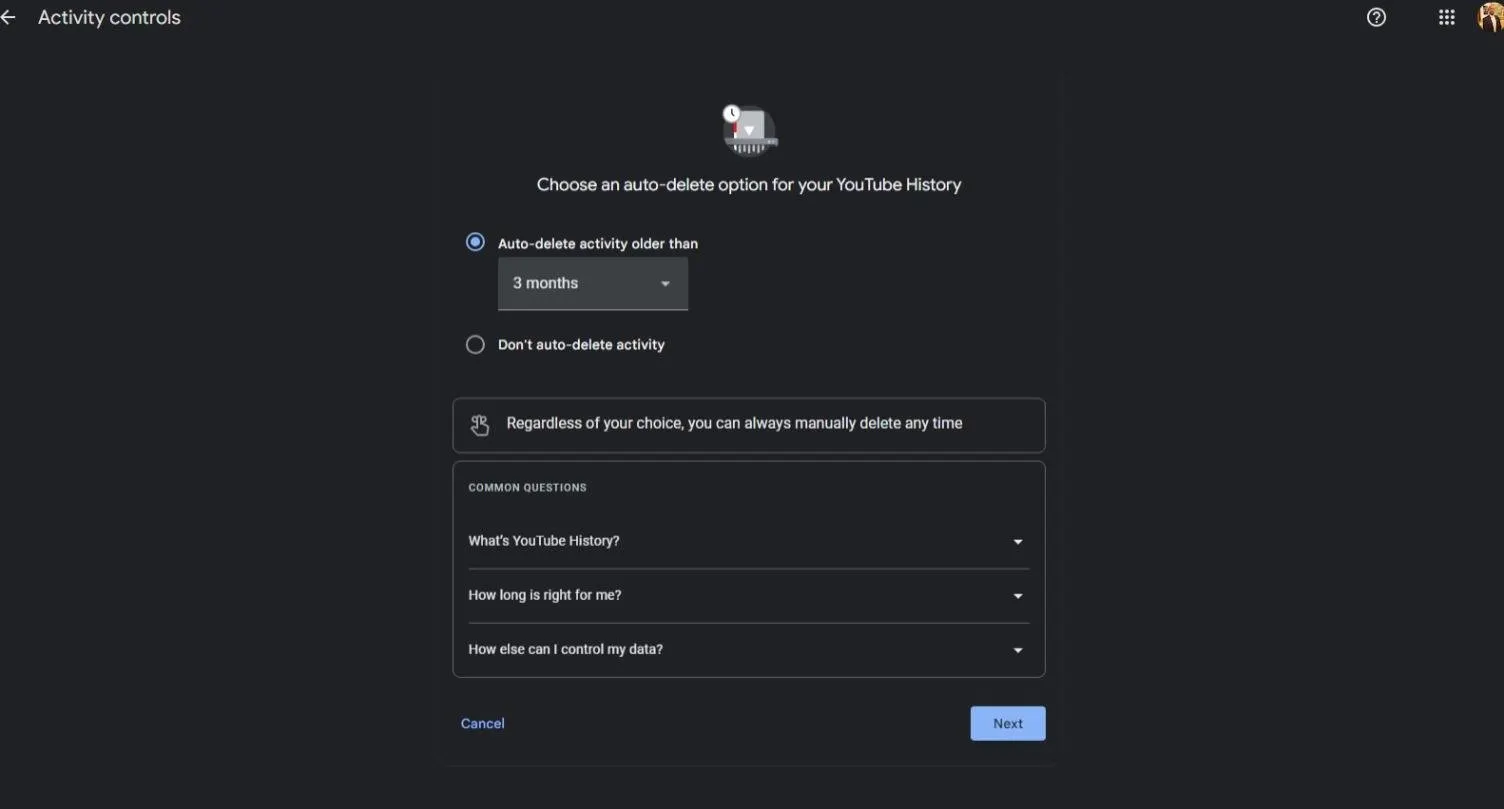
Copilot
In September, Microsoft added its Copilot generative AI model to its Microsoft 365 suite of business tools, its Microsoft Edge browser, and Bing search engine. Microsoft also included a preview version of the chatbot in Windows 11. In December, Copilot was added to the Android and Apple app stores.
Microsoft does not provide the option to opt out of having user data used to train its AI models, but like Google Gemini, Copilot users can delete their history. The process is not as intuitive on Copilot, however, as previous chats still show on the desktop version’s home screen even after being deleted.
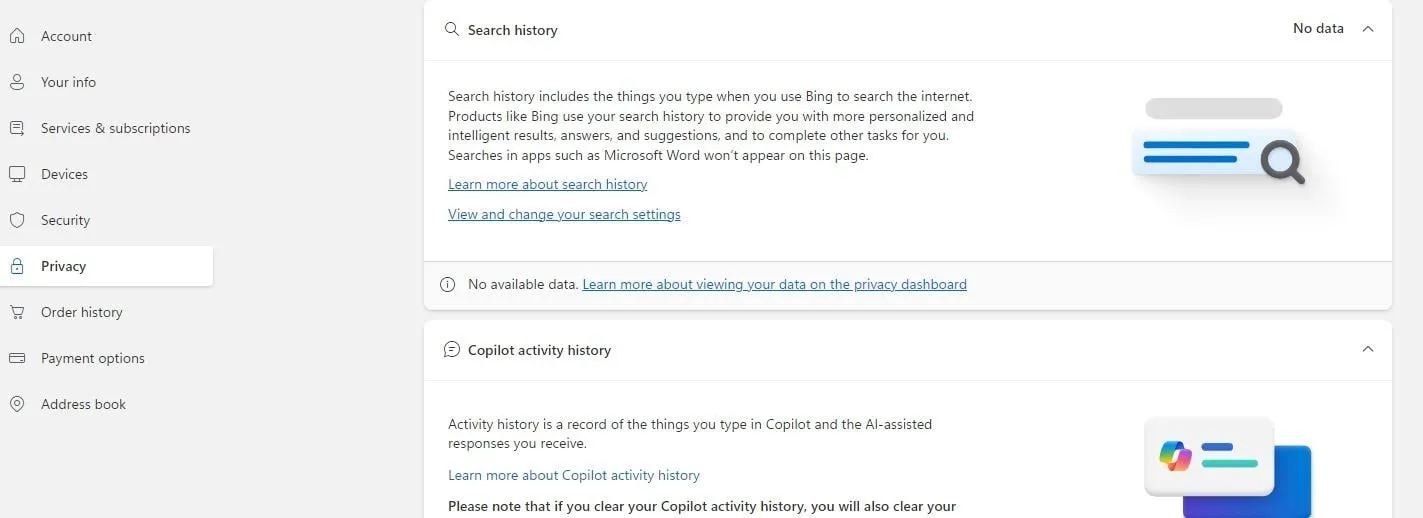
To find the option to delete Copilot history, open your user profile at the top right of your screen (you must be signed in) and select “My Microsoft Account.” On the left, select “Privacy,” and scroll down to the bottom of the screen to find the Copilot section.
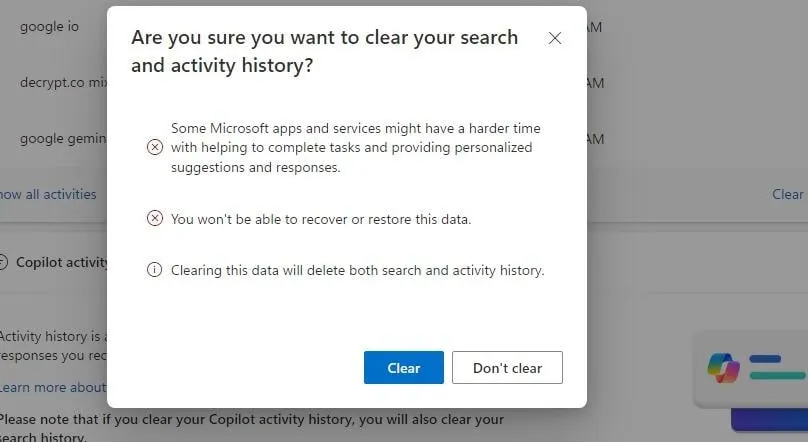
Because Copilot is integrated into Bing’s search engine, clearing activity will also clear search history, Microsoft said.
A Microsoft spokesperson told Decrypt that the tech giant protects consumers’ data through various techniques, including encryption, deidentification, and only storing and retaining information associated with the user for as long as is necessary.
“A portion of the total number of user prompts in Copilot and Copilot Pro responses are used to fine-tune the experience,” the spokesperson added. “Microsoft takes steps to de-identify data before it is used, helping to protect consumer identity,” adding that Microsoft does not use any content created in Microsoft 365 (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook, Teams) to train underlying “foundational models.”
Meta AI
In April, Meta—the parent company of Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp—rolled out Meta AI to users.
“We are releasing the new version of Meta AI, our assistant, that you can ask any question across our apps and glasses,” Zuckerberg said in an Instagram video. “Our goal is to build the world’s leading AI and make it available to everyone.”
Meta AI does not provide users the option to opt out of having their inputs used to train the AI model. Meta does give the option to delete past chats with its AI agent.
To do so from a desktop computer, click the Facebook settings tab at the bottom left of your screen, located above your Facebook profile image. Once in settings, users have the option to delete conversations with Meta AI.
Meta does explain that deleting conversations here will not delete chats with other people in Messenger, Instagram, or WhatsApp.
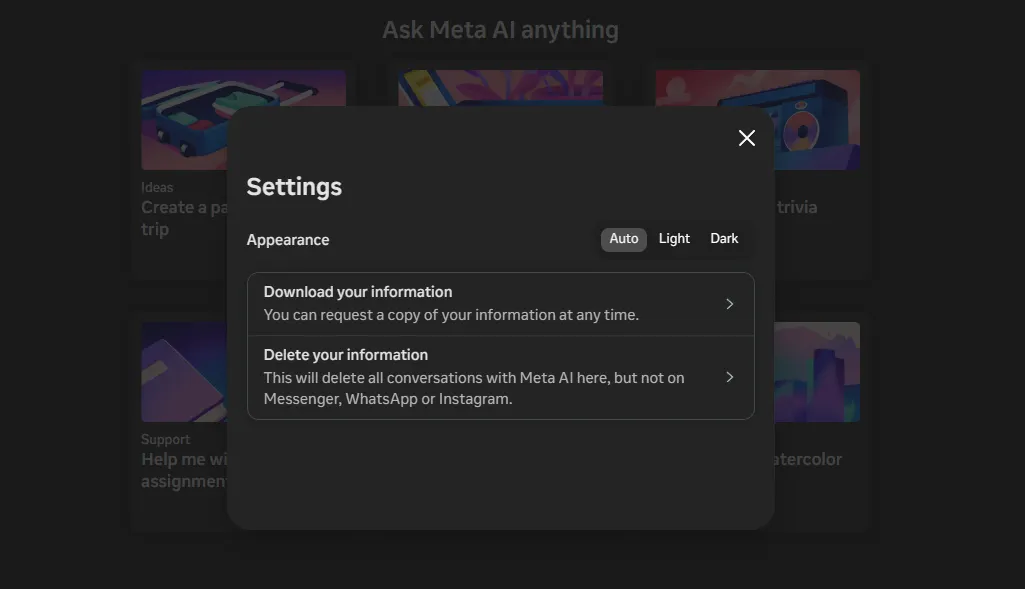
A Meta spokesperson declined to comment on whether or how users could exclude their information from being used in Meta AI model training, instead pointing Decrypt to a September statement by the company about its privacy safeguards and the Meta settings page on deleting history.
“Publicly shared posts from Instagram and Facebook—including photos and text—were part of the data used to train the generative AI models,” the company explains. “We didn’t train these models using people’s private posts. We also do not use the content of your private messages with friends and family to train our AIs.”
But anything you send to Meta AI will be used for model training—and beyond.
“We use the information people share when interacting with our generative AI features, such as Meta AI or businesses who use generative AI, to improve our products and for other purposes,” Meta adds.
Conclusion
Of the major AI models we included above, OpenAI’s ChatGPT provided the easiest way to delete history and opt-out of having chatbot prompts used to train its AI model. Meta’s privacy practices appear to be the most opaque.
Many of these companies also provide mobile versions of their powerful apps, which provide similar controls. The individual steps may be different—and privacy and history settings may function differently across platforms.
Unfortunately, even cranking all privacy settings to their tightest levels may not be enough to safeguard your information, according to Venice AI founder and CEO Erik Voorhees, who told Decrypt that it would be naive to assume your data has been erased.
“Once a company has your information, you can never trust it’s gone, ever,” he said. “People should assume that everything they write to OpenAI is going to them and that they have it forever.”
“The only way to resolve that is by using a service where the information does not go to a central repository at all in the first place,” Voorhees added—a service like his own.
Edited by Ryan Ozawa.